Earth Materials, Processes and Environments
GEOL-1121 Fall 2014
Review Questions for 4th Test
Chapters 12 and 13
Running Water ‑ Rivers and Streams (Chapter 12)
1) Describe the various processes involved in the Hydrologic Cycle? What is the importance of streams and groundwater in this cycle? Describe how changes or disruption of this cycle could cause several problems to modern society. What are the two major driving forces that keep Earth's water supply in motion?
2) Describe how water supplies are cleansed or purified by the water cycle. Why are temperature changes usually associated with these processes? How will climate change alter the hydrologic cycle?
3) Describe how the movement of water on the land surface reshapes the landscape over time. What percentage of Earth’s water supply is fresh water that is not locked in ice caps? What percentage of Earth’s water is found in streams and rivers? Why does this small amount of Earth’s water so important? Stream water accounts for how much of human usage?
4) Describe how the discharge of a stream is measured. Be able to calculate stream discharge provided that stream width, height and water velocity are given.
5) What is the longitudinal profile of a stream? What is meant by an equilibrium profile or graded stream? What are some of the ways in which the base level of a stream can change? Give examples of both local and ultimate base levels.
6) Describe how a stream adjusts to changes in base level. Explain why most man-made lakes usually fill with mud over a period of 50 to 100 years.
7) Name and describe the different ways in which sediment can be carried by a stream. Where are these different components most commonly deposited? What factors determine how much material can be carried by a stream?
8) Describe how turbulent flow and settling velocity determine the amount and size of material that is carried in suspension. Describe the factors that control the type of flow in a river. In which type of streams does laminar flow most commonly occur?
9) Name and describe three important types of drainage patterns. How do these differ from the channel types? Which type of drainage pattern and channel type is most typical of the Coastal Plain?
10) Describe the 3 major types of sedimentary deposits associated with meandering streams. Where do these deposits form?
11) Compare and contrast alluvial fan and delta deposits.
12) Describe how a floodplain forms. How does a floodplain differ from a stream terrace?
13) Describe how incised meanders form. Where is an example of incised meander loop in the continental United States?
14) Describe some of the structures and techniques that are used to prevent river and stream flooding. How are streams and rivers also used as a major source of renewable energy? What are some of the problems with these structures?
15) Define the following terms: graded bedding, gradient, gauging station, oxbow
lake, pothole, dendritic, distributary, and sandbar.
Groundwater (Chapter 13)
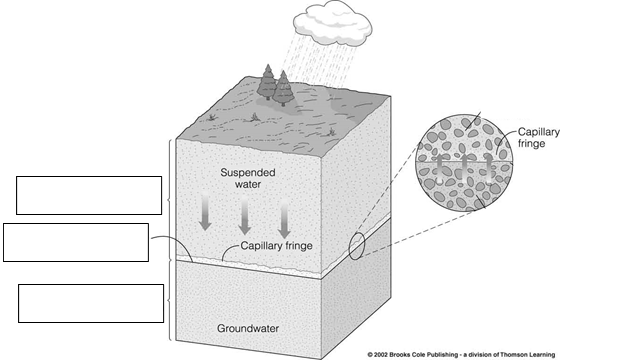
1) Describe the occurrence and distribution of groundwater. What percentage of earth’s water is found as groundwater? What percentage of human usage is this water source? On the diagram shown below, label the zone of saturation, zone of aeration and the water table. Wells are drilled into which of these layers?
2) What controls the rate or velocity at which groundwater travels? (ie. What is Darcy's Law?) What is the average velocity of groundwater movement? What is the force that drives groundwater?
3) What is the water table? Why is the water table such an irregular surface?
4) Many of the streams in the southwestern United States are influent, while most of the streams around Americus are effluent. What does this mean? What controls the formation of each type?
5) Define and describe porosity and permeability. Why are these properties important in the formation of an aquifer? Name a rock type or sediment that has high porosity, but low permeability. Name a rock or sediment type that has both high porosity and high permeability.
6) What is an aquiclude? Describe the properties of an aquiclude?
7) What is a spring? Describe two ways in which a spring can form. Would they always flow freely onto the ground surface?
8) Describe the different problems associated with groundwater overuse. Include a discussion of subsidence, cone of depression, and saltwater incursion. Suggest possible solutions to these problems.
9) Groundwater pollution is becoming a widespread problem. Describe some of the ways in which groundwater can become polluted and ways in which it can be rectified. How does arsenic get into some drinking water? Why is it considered toxic?
10) Describe how home septic tanks clean sewage and prevent harmful bacteria from getting into water supplies. Describe some of the problems with these systems.
11) What is karst topography? How does it form? How do most underground cave systems form? Name and describe some of the other typical land features
associated with karst topography.
12) Compare and contrast the following: artesian wells,
pumped wells, sinkholes, hot springs, recharge
and discharge.