Earth Materials, Processes and Environments
GEOL-1121 Fall 2015
Practice for Lecture Test #3
Name_______________________________
PART I ‑ Multiple Choice (50 points ‑ 2 points each question)
**Circle the letter of the best answer.
1) Lithostatic pressure results from:
a) The weight of overlying rocks during burial.
b) Directed pressures during plate tectonic collisions.
c) Combined heating and applied pressure during regional metamorphism.
d) Pressures associated with deep-seated faults.
2) Which of the following minerals is most easily changed or altered by metamorphism?
a) Quartz
b) Calcite
c) Clay
d) Muscovite
3) How does heat and increased temperature change rock material during metamorphism?
a) It melts the rock allowing new minerals to form.
b) It results in expansion and weakening of atomic bonds allowing mineral change.
c) It causes compaction and cementation of the rock material.
d) All of the above
4) Which of the following is the most common protolith (parent rock) of a marble:
a) Basalt
b) Diorite
c) Shale
d) Limestone
5) Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are classified according to:
a) Grain size
b) Composition
c) Texture
d) All of the above
6) A gneiss forms under which of the following conditions?
a) Strong directed pressures and high temperatures.
b) Strong lithostatic pressures and high temperatures.
c) Low pressures, high temperatures and extensive chemical fluid interaction.
d) Strong directed pressures and low temperatures.
7) Which of the following statements about dynamic metamorphism is correct?
a) It commonly forms mylonite.
b) It is characterized by strong directed pressures.
c) It associated with deep-seated faults.
d) All of the above
8) Hydrothermal deposits of precious metals are commonly associated with:
a) Burial metamorphism
b) Dynamic metamorphism
c) Contact metamorphism
d) Regional metamorphism
9) Which of the following textures is not a type of foliation?
a) Granoblastic texture
b) Slaty cleavage
c) Gneissic layering
d) Slaty cleavage
10) Which of the following statements about metamorphic rocks in general is correct?
a) They provide important clues about deformational events, such as continental collisions and mountain building.
b) All metamorphic rocks display foliation.
c) They form under a limited range of temperature, pressure and chemical conditions.
d) All of the above
11) Areas of metamorphic rock that are characterized as having the same metamorphic index mineral are described as having the same:
a) Facies
b) Foliation
c) Grade
d) Zone
12) Which of the following statements concerning the geobaric gradient is correct?
a) It results from the weight of overlying rocks.
b) It is approximately 4,410 psi/km.
c) It is a measure increase in the lithostatic stress with increase in depth.
d) All of the above
13) Which of the following statements concerning the Al2SiO5 polymorphs is correct?
a) They include kyanite.
b) They serve as index minerals in metamorphic rocks.
c) They have the same composition and but different atomic structure.
d) All of the above.
14) Which of the following statements concerning S- or secondary waves is correct?
a) They will not pass through liquids.
b) The cause substantial damage to man-made structures during earthquakes.
c) They move through the material by elastic dilation and compression.
d) All of the above
15) Which of the following is the most widely-accepted theory that explains the cause of earthquakes?
a) Bowen’s Displacement Theory
b) Plastic Displacement Theory
c) Elastic Rebound Theory
d) Plastic-Brittle Behavior Theory
16) Most earthquakes occur in which of the following areas?
a) At depths greater than 100 kilometers
b) At depths less than 100 kilometers
c) Throughout the crust and all of the mantle
d) In the asthenosphere
17) The focus and epicenter of an earthquake are the same point when:
a) Initial offset or movement occurs at depth below a steeply inclined fault.
b) Initial offset or movement along the fault occurs at the surface.
c) Initial offset or movement along the fault occurs in the ocean.
d) All of the above
18) Which of the following is a good way to prevent earthquake damage?
a) Build only on unconsolidated water-saturated sediments.
b) Lock up all active faults and try to prevent even the smallest movement.
c) Build more flexible structures in earthquake areas.
d) All of the above
19) Tsunami are caused by:
a) Rapid displacement of large segments along faults on the ocean floor.
b) A combination of extreme tides and earthquake waves.
c) Subsidence of large volcanic islands and inflowing seawater.
d) All of the above
20) Which of the following is used in determining the location of an earthquake?
a) Differences in the arrival times of the P- and S-waves at the seismic station.
b) Differences between the heights of the P- and S-waves at the seismic station.
c) Differences in the shape of the P- and S-waves at the seismic station.
d) Astrology studies and psychic readings.
21) The seismic waves of an earthquake with a Richter magnitude of 5.0 are how much larger (relative to amplitude or wave height) than an earthquake with magnitude of 3.0?
a) Two times larger
b) Ten times larger
c) One hundred times larger
d) One thousand times larger
22) Which of the following is not commonly used in earthquake prediction?
a) Studies of previous seismic activity
b) Field studies of faults and fracture systems.
c) Extremely precise laser measurements of ground deformation.
d) Simple electronic warning devices along most active faults.
23) Which of the following statements concerning the MOHO is correct?
a) It is the boundary between the mantle and the crust.
b) It is recognized by a decrease in seismic wave velocities.
c) It results from a change in density but not composition.
d) All of the above
24) Liquefaction involves which of the following materials?
a) Water-saturated sediments
b) High-temperature rock material
c) Slightly-fractured bedrock
d) Partially-molten igneous rocks
25) The San Andreas is located along which of the following?
a) Transform Plate Boundary
b) Subduction Zone
c) Divergent Ocean-Continent Plate Margin
d) Convergent Continent-Continent Plate Margin
PART II ‑ Fill in the Blank (50 pts. ‑ 2 pts. each question)
26) The major focus of this class is: ________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________
27) Metamorphic rocks are classified according to ___________________ and ______________________.
28-30)(6pts) On the diagram shown below, label the fields (shown with dashed lines) that define sedimentary rock formation, igneous rock formation and the various types of metamorphism (contact, regional, burial and dynamic).
 |
31-32) The two most important controls on the mineral composition of the metamorphic rocks are ________________________________ and ____________________________________.
33-34) Provide the best estimate for the geothermal gradient for the upper crust (Be sure to include units. ______________________. Using this gradient, determine the temperature at 5 kilometers below the surface. _______________________
35) Explain why contact metamorphism is limited in extent when it occurs. ______________ _______________________________________________________________________
36) Explain why quartz does not serve as a good index mineral in metamorphic rocks. _____________________________________________________________________
37) ____________________ textures form in monomineralogic (single mineral) rocks with equidimensional grains when subjected to regional and/or burial metamorphism.
38) ______________ is a fine-grained laminated fault rock formed by dynamic metamorphism.
39) Rocks will initially display ________________ behavior as stress as stress starts to accumulate and the rock is deformed but not broken. If the strength of the rock material is surpassed, the rocks will break as a result of _________________ behavior instantaneously releasing the stress and often causing earthquakes.
40) The sudden loss of strength and movement of water-saturated sediments due to seismic waves is called ________________________.
41) An older measurement of earthquake intensity based on human observations and structural damage is called the ___________________________.
42) The point along a fault or fracture where movement originates and the earthquake is generated is called the _________________; whereas the location on the Earth’s surface directly above this point is called the ___________________.
43) Describe the seismic and geologic evidence that indicates the Earth has an iron-rich liquid outer core. _________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________
44) The deformable layer of the mantle located between the depths of 100 and 250 kilometers that appears responsible for plate tectonic movement is called the ___________________.
45) Explain why tsunami are more common along the margin of the Pacific Ocean than around the Atlantic. ____________________________________________________________
46-47) In addition to damage to rigid man-made structures, list two other common causes of earthquake destruction. ________________________ and ________________________
48) Explain why most earthquakes occur in the upper 100 km and not deeper levels within the Earth. _____________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________
49-50) What does it mean if a seismic station receives the S-waves almost immediately after the P-waves and all the waves are relatively small on the seismograph? ____________________ __________________________________________________________________________
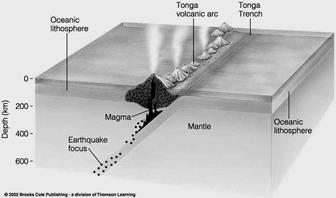 |
Extra Credit (2 points): The above picture shows an area of inclined seismic activity associated with a subduction zones. It is called a __________________________ Zone.